Computer vision is a riveting and revolutionary field. It endeavors to understand and replicate human visual perception through various sensor types, essentially enabling machines to interpret the reality around us.
Indeed, Computer Vision could be termed as the art of enabling machines to see.
The intricacies of how we see things are taken for granted, as the process seems natural and automatic. However, the same cannot be said for machines. The science of computer vision doesn’t solely entail machines “seeing” things; it encompasses interpreting these images, recognizing objects, understanding the context, and making decisions based on these interpretations. It’s about translating bytes in memory into actionable information.
Through computer vision, we empower machines to “see” and “interpret” the world, unlocking a plethora of potential applications. Welcome to the brave new world of pixels!
Computer Vision: The Art of Teaching Machines to See
Our most dominant sense is vision, with approximately 60% of our brain dedicated to visual perception. This fact lies at the heart of computer vision, whose goal is to make machines “see”. This discipline faces the daunting task of equipping machines to interpret the world as humans do, such as recognizing complex or unconventional objects.

The process of computer vision is intricate, as machines must capture, process, and interpret light rays from the external world to form an understanding of objects. This task is complex, and our current technology is far from matching the detailed accuracy and rich detail with which a small child can describe an object.
To grasp the challenge of this inverse problem, consider the following figure. While we perceive reality through our external senses and formulate concepts of objects through our intellect (tied to the soul in a metaphysical conception), a computer only sees… numbers. For those who wish to delve deeper into the theory of image formation, I recommend this theoretical article I recently wrote.
![]()
Image Processing vs Computer Vision
For those new to the realm of data science, particularly in the domain of images, differentiating two fundamental concepts may be challenging.
Image processing encompasses techniques to enhance or emphasize features of an image, either to improve its quality or to spotlight specific aspects. For instance, you could apply an image processing technique to a photo to accentuate the edges of objects or eliminate the background. These techniques manipulate the image and highlight features but do not independently generate additional information.
In contrast, computer vision aims to extract significant information from images or videos, converting raw data into actionable insights. It’s a more analytical process that employs predictive models and exploratory analyses to draw insights from images. For example, facial tracking in a video can produce a 3D model of a face applicable in various contexts, ranging from augmented reality applications to facial recognition.
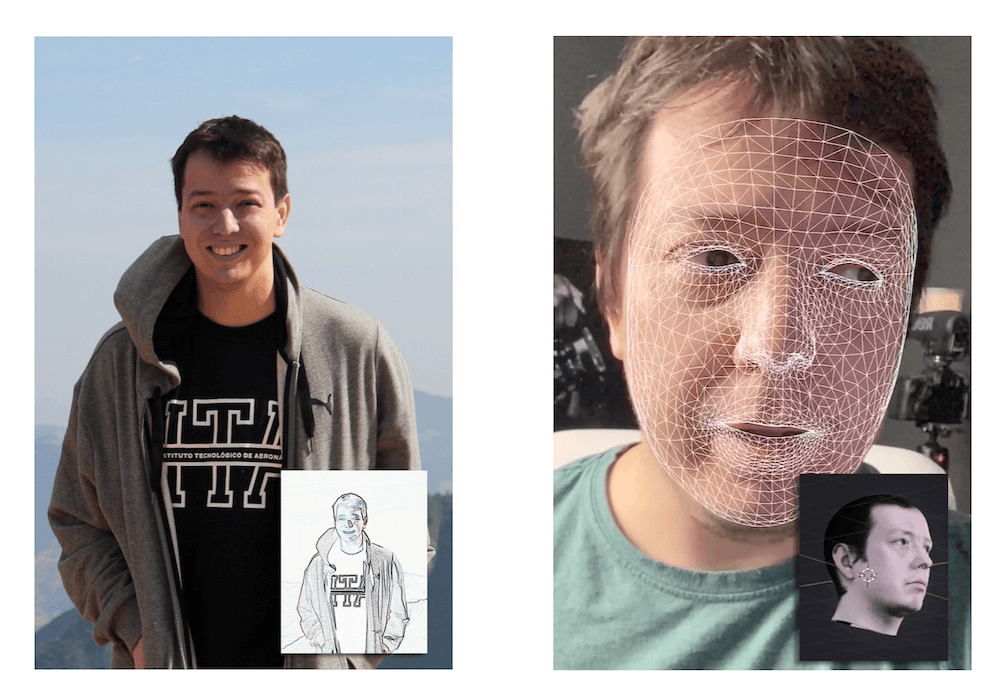
In a simplified context, while image processing involves direct image manipulation, computer vision uses the processed image to extract information and insights. Therefore, although these are distinct fields, they are complementary and often coexist in numerous data science projects.
Potential Applications
Modeling the visual world is far more complex than modeling phenomena such as spoken sound production. However, despite these challenges, vision algorithms have already found successful real-world applications. I have highlighted several project examples on this blog, including a fatigue detector, drone surveillance system, real-time 3D mapping, and more. Additionally, here is a more comprehensive list of potential applications:
- Augmented and Virtual Reality: Computer vision is the fundamental technology that allows devices to recognize and interact with the physical environment, essential for creating immersive augmented and virtual reality experiences.
- Machine Inspection: Rapid inspection of parts for quality assurance using stereoscopic vision with specialized lighting to measure tolerances on aircraft wings or automobile body parts, or look for defects in steel castings using X-ray vision.
- Super-resolution Imaging: This technique uses computer vision to improve the spatial resolution of digital images, overcoming the physical limitations of the imaging system and providing higher quality and clearer images.
- Optical Character Recognition (OCR): OCR technology, enabled by computer vision, allows computers to read and recognize text in digital images or scanned documents, facilitating tasks that would require manual data entry, such as scanning old records or extracting text from handwritten documents.
- Retail: Object recognition for automated checkouts and fully automated stores.
- Object Recognition: Computer vision is used to recognize and classify objects in images and videos. This has varied applications, from facial recognition in security software to motion analysis in surveillance and sports videos.
- Medical Imaging: Computer vision can be used to analyze medical images, such as X-rays and magnetic resonance images, to identify and diagnose medical conditions.
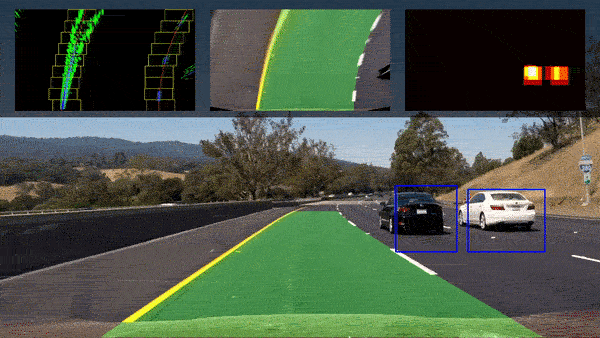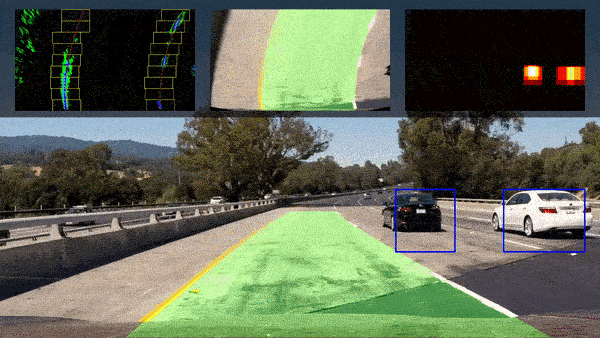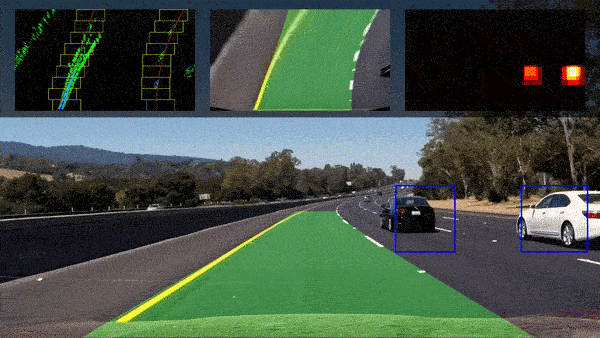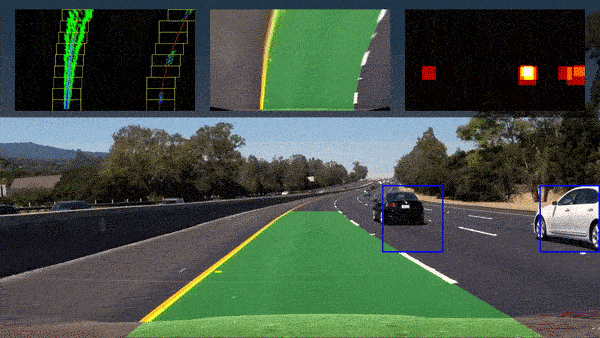
- Autonomous Vehicles: Capable of driving from point to point between cities, as well as autonomous flight.
- Quality Control: In manufacturing, computer vision can be used to inspect products for defects, such as scratches or dents on surfaces.
- Robotics: Computer vision is used in robotics to enable machines to identify and interact with objects in the environment.
- Agriculture: In agriculture, computer vision can be used to monitor the growth and health of crops, identify pests and optimize crop yields.
- 3D Model Construction (photogrammetry): Fully automated construction of 3D models from aerial and drone photographs.
In short, computer vision has extensive potential applications across various industries. As the technology continues to advance, we can anticipate increasingly innovative uses for this potent technology.
Salary for a Computer Vision Engineer
The salary of a Computer Vision Engineer can vary significantly depending on factors such as location, industry sector, professional experience, and specialization. However, based on salary statistics and reports, the average salary for this role in the United States ranges from $120,000 to $150,000 annually, with potential for higher earnings depending on the company and seniority level.
In Brazil, although salaries tend to be lower compared to the United States, Computer Vision professionals are among the highest-paid in the technology field, with salaries ranging from R$108,000 to R$180,000 per year.
This is a rapidly evolving career, with increasing demand in sectors like automotive, retail, health, logistics, and many others that are progressively implementing computer vision-based solutions. Thus, the career prospects and earning potential for computer vision engineers are very promising.
Skills Required for a Computer Vision Engineer
Being a Computer Vision Engineer requires mastery of several disciplines simultaneously. Python and C++ are the most sought-after programming languages. Tesla, for instance, typically trains its models and prototypes features in Python, deploying the product in C++ at a later stage.
Theoretically, essential skills involve knowledge of mathematics, specifically calculus and linear algebra. Furthermore, a Computer Vision Engineer should be proficient with libraries such as TensorFlow, PyTorch, and OpenCV.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the field of computer vision is a rapidly growing discipline with transformative implications across various sectors. It combines intricate elements of image processing, machine learning, and mathematics to endow machines with the capacity to “see” and understand the world as we do.
The successful application of computer vision technologies brings a wealth of benefits, enabling efficiencies and opportunities that were previously inconceivable. As computer vision engineers, the opportunity lies in continuing to develop and refine these technologies, pushing the boundaries of what machines can perceive and understand.
The future of computer vision is promising, with far-reaching implications for our world and our interaction with machines.














