Monocular Depth Estimation is a Computer Vision task that involves predicting the depth information of a scene, that is, the relative distance from the camera of each pixel, given a single RGB image. This challenging task is a key prerequisite for scene understanding for applications such as 3D scene reconstruction, robotics, Spatial Computing (Apple Vision Pro and Quest 3), and autonomous navigation.

While various approaches have been developed for depth estimation, Depth Anything represents today a significant advancement in the field of monocular depth perception. In this article, we will explore some of the theoretical foundations of monocular depth perception, and we will clone the Depth Anything repository to conduct our own tests in a local development environment.
Monocular Depth Perception
Depth perception is what allows us to interpret the three-dimensional world from two-dimensional images projected on our retinas. This ability evolved as a crucial aspect for survival, enabling humans to navigate the environment, avoid predators, and locate resources.
The human brain accomplishes this feat through a series of interpretations of visual information, where the overlap of the binocular visual field provides a rich perception of depth.
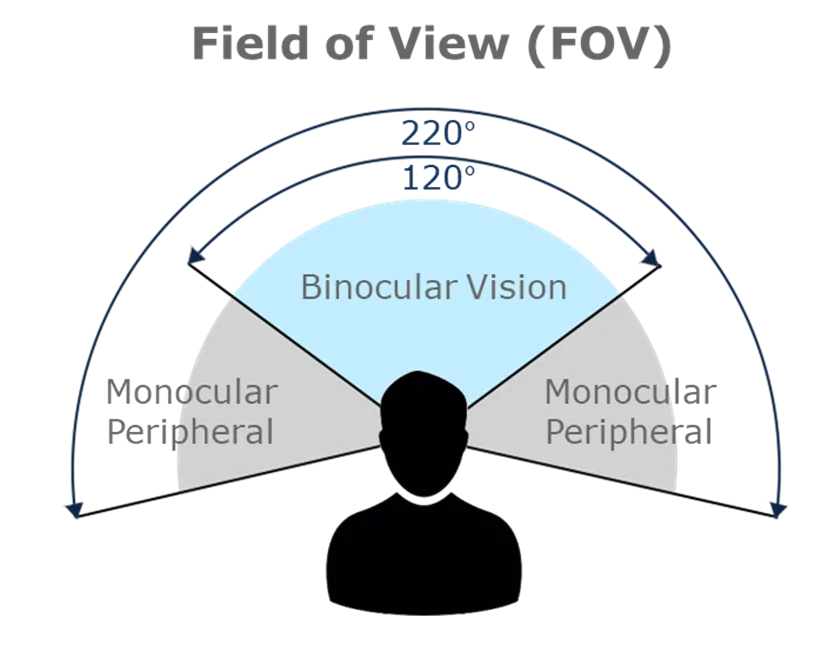
In addition to binocular vision, this perception is enriched by various monocular cues (depth cues), elements in the environment that allow a single observer to infer depth even with one eye closed. Among these cues are occlusion, relative size, cast shadows, and linear perspective.
These same principles and mechanisms of perception find a parallel in Computer Vision, where the essence of estimation also lies in capturing the spatial structure of a scene to accurately represent its three-dimensional aspects.
Depth Anything for Depth Estimation
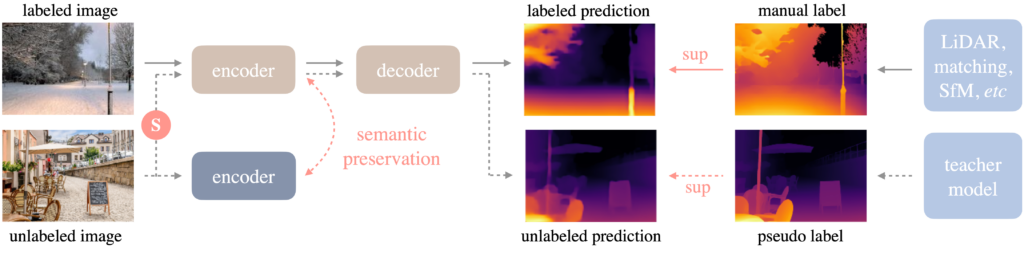
The Depth Anything model, introduced in the work “Depth Anything: Unleashing the Power of Large-Scale Unlabeled Data”, represents a significant advancement in monocular depth estimation. Based on the DPT (Dense Prediction Transformer) architecture, it was trained on a vast dataset of over 62 million unlabeled images.

The success of this approach is attributed to two main strategies.
- The use of data augmentation tools to establish a more challenging optimization target.
- Use of auxiliary supervision to ensure the inheritance of semantic priors from pre-trained encoders.
The generalization capability of Depth Anything, tested on six public datasets and randomly captured photographs, surpassed some metrics of existing models, such as MiDaS v3.1 and ZoeDepth.
If you want to delve deeper into the materials and methods used in the research, access the original article at this link.
Setting Up the Environment for “Depth Anything”
To start using Depth Anything for monocular depth estimation, it’s necessary to prepare your development environment by following some simple steps. Make sure you have Poetry installed.
To clone the repository and install dependencies, follow the steps described below:
1. Clone the Repository: First, clone the project repository using the command in the terminal:
git clone https://github.com/LiheYoung/Depth-Anything.git
2. Access the Project Directory: Next, access the project directory:
cd Depth-Anything
3. Initialize the Environment with Poetry: If it’s your first time using Poetry on this project, initialize the environment:
poetry init
4. Activate the Virtual Environment: Activate the virtual environment created by Poetry:
poetry shell
5. Install Dependencies: Install the necessary dependencies, including Gradio, PyTorch, torchvision, opencv-python, and huggingface_hub:
poetry add gradio==4.14.0 torch torchvision opencv-python huggingface_hub
6. Run the Application: Run the application using Streamlit with the command:
python app.py
With the Streamlit app running, you can upload your photos directly through the UI. If you have any difficulties installing the dependencies on your computer, you can also test Depth Anything in this official demo.
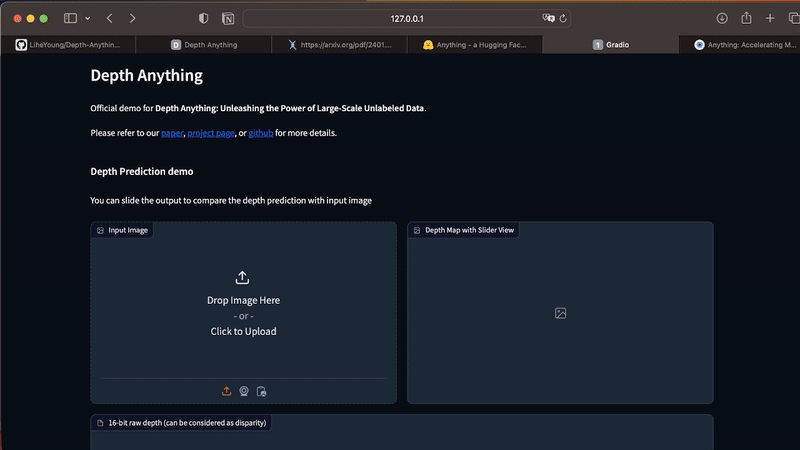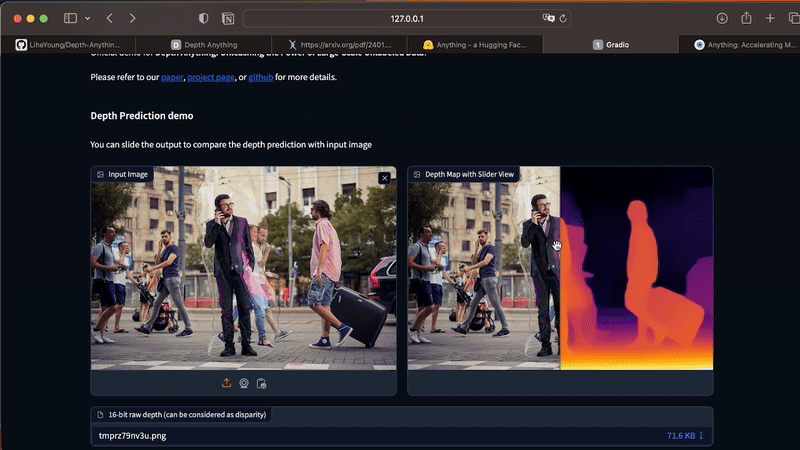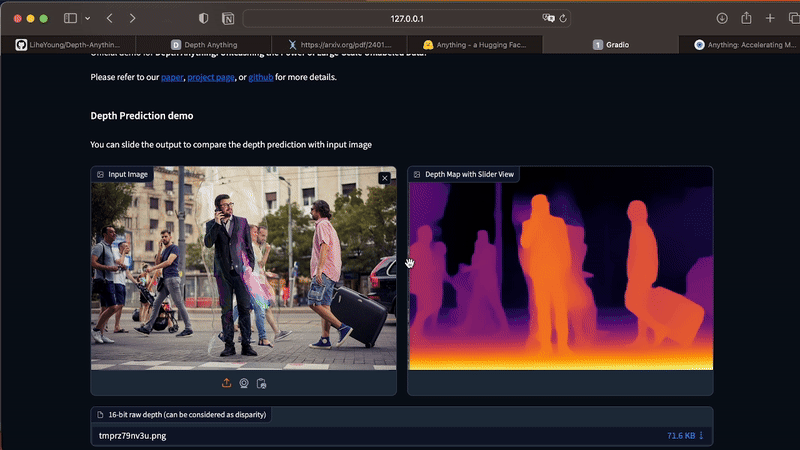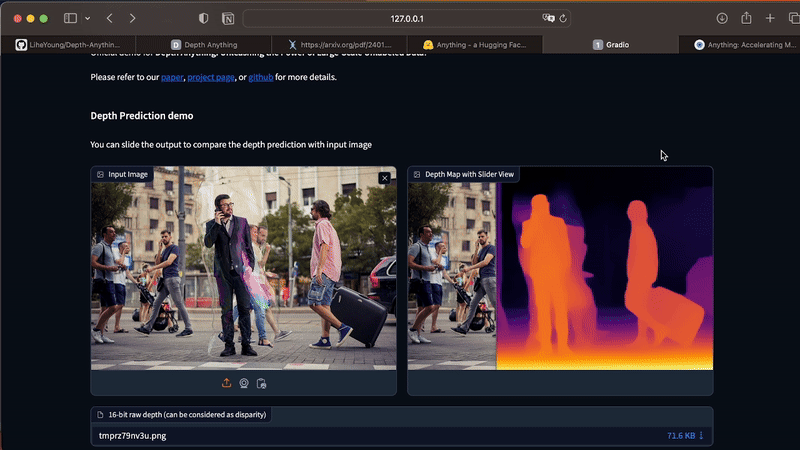
The app works only for static images. To generate depth maps from videos, execute the command below in your Terminal. As this process is costly in terms of processing, I recommend that you start your tests with short videos, between 3 and 10 seconds.
python run_video.py --encoder vitl --video-path /path/to/your/video.mov --outdir /path/to/save
Takeaways
- Essence of Monocular Depth Perception: Monocular depth estimation is crucial for understanding the spatial structure of a scene from a single image, enabling applications such as 3D scene reconstruction.
- Advancements with Depth Anything: Representing a significant leap in monocular depth perception, the Depth Anything model utilizes the DPT architecture and was trained on an extensive dataset, showing excellent generalization capability.
- Environment Setup: A step-by-step guide to setting up the development environment to use Depth Anything, including installing dependencies and running applications for practical tests.
- Practical Application: The article provides detailed instructions for testing depth estimation with images and videos, facilitating practical experimentation and visualization of the Depth Anything model’s results.














